Research Updates
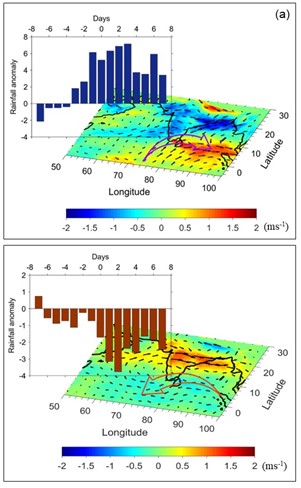
In this study, the characteristic features and possible precursors for wet and dry spells of rainfall over southern tip of India are investigated. We also explore the variability in monsoon low-level jet (LLJ) in relation to wet and dry spells over a coastal station Thiruvananthapuram (8.48°N, 76.95°E) in southwest India using in-situ observations and other ancillary datasets. The results show that a wet spell spanning 3-4 days contributes about 30% of seasonal rainfall.Wet spells are characterized by westerly wind anomaly in the southern tip of India and easterly wind anomaly in northern India, leading to anomalous cyclonic vorticity over the Indian subcontinent. The opposite happens during dry spells. These characteristics are prominent from two days prior to the initiation of the spells, suggesting they may be used as precursors for forecasting wet and dry spells over Thiruvananthapuram. Analysis of low- to mid-tropospheric (2 and 4 km) humidity reveals significant moistening (drying) during wet (dry) spells. Yet, both wet and dry spells experience humid (>80%) boundary layer. The differences in mid-level humidity and thermodynamical structures between wet and dry spells seem to contribute to distinct rainfall characteristics over the southern tip of India. These results indicate that the use of in-situ observations along with large-scale reanalysis datasets may provide valuable information on the precursors for wet and dry spells over the southern tip of India, which can help both in regional- and city-level planning and management of water resources.Composite anomaly of zonal winds (ms-1) overlaid with vector at 850 hPa on d-2 day in (a) wet spells and (b) dry spells. Anomalies were calculated after subtracting the climatological daily mean for 1981-2020. The southerly winds from the Arabian Sea and westerlies in the Bay of Bengal strengthened at 5°N latitude (marked with purple curved arrow) on d-2 day at 850 hPa level that acts as the primary precursor for the wet spells. The easterly wind anomalies developed over the equatorial Indian Ocean located to the south and southwest of the southern tip (marked with red curved arrow), act as a precursor for the onset of dry spells. The corresponding, temporal evolution (±8 days) of rainfall anomalies (mm) averaged over the southern region (70°-85°E, 5°S-15°N) in wet and dry spells are represented as bar graph.
Bibliographic Info: Resmi, E. A., Preethi, B., Ajayamohan, R. S., Ray, P., Unnikrishnan, C. K., Nita, S., Sumesh, R. K., & Dharmadas, J. (2023). Analysis of localized features during wet and dry rainfall episodes over southern tip of India. International Journal of Climatology, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.8267.
 The Ediacaran-Cambrian transition period was one of the most significant intervals in the Earth’s history. Widespread changes in the oceanic and atmospheric conditions characterized this interval, which likely triggered the radiation of metazoans. Much of our knowledge of these changes have come from geochemical studies of marine carbonates deposited during this time. In search of such information and to establish the true geographical extent of these events, we carried out a detailed field and geochemical investigation in the Bilara Group of the Marwar Supergroup, the youngest Proterozoic marine carbonate succession of peninsular India. The variations in the 87Sr/86Sr observed in the limestone formation of the Bilara Group (0.70810 to 0.70916) suggest an early Cambrian (520–539 Ma) depositional age for the Group. We identify two δ13C negative excursions of magnitudes ~6‰ and ~7‰, respectively, in the middle and lower parts of the Bilara Group. Since these δ13C anomalies are observed through-out the Marwar Basin that was connected to global oceans, we believe that they represent temporal changes in the chemistry of seawater. Using the principles of δ13C stratigraphy and the available geochronological information, we correlate the middle Bilara anomaly to the Shiyantou carbon isotope excursion (SHICE). Although, poor age constraints hinder a definitive correlation of the older Bilara anomaly, we speculate that it is the basal Cambrian carbon isotope excursion (BACE). These results place the Ediacaran-Cambrian boundary closer to the basal part of the Bilara Group in the Marwar Supergroup.
The Ediacaran-Cambrian transition period was one of the most significant intervals in the Earth’s history. Widespread changes in the oceanic and atmospheric conditions characterized this interval, which likely triggered the radiation of metazoans. Much of our knowledge of these changes have come from geochemical studies of marine carbonates deposited during this time. In search of such information and to establish the true geographical extent of these events, we carried out a detailed field and geochemical investigation in the Bilara Group of the Marwar Supergroup, the youngest Proterozoic marine carbonate succession of peninsular India. The variations in the 87Sr/86Sr observed in the limestone formation of the Bilara Group (0.70810 to 0.70916) suggest an early Cambrian (520–539 Ma) depositional age for the Group. We identify two δ13C negative excursions of magnitudes ~6‰ and ~7‰, respectively, in the middle and lower parts of the Bilara Group. Since these δ13C anomalies are observed through-out the Marwar Basin that was connected to global oceans, we believe that they represent temporal changes in the chemistry of seawater. Using the principles of δ13C stratigraphy and the available geochronological information, we correlate the middle Bilara anomaly to the Shiyantou carbon isotope excursion (SHICE). Although, poor age constraints hinder a definitive correlation of the older Bilara anomaly, we speculate that it is the basal Cambrian carbon isotope excursion (BACE). These results place the Ediacaran-Cambrian boundary closer to the basal part of the Bilara Group in the Marwar Supergroup.
Bibliographic Info: Bivin G. George, Sanjeev Kumar, Jyotiranjan S. Ray [2021]. C-Sr isotope stratigraphy of carbonate formations of the late Neoproterozoic - Cambrian Marwar supergroup, western India. Precambrian Research, Vol. 364, Art. 106378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2021.106378
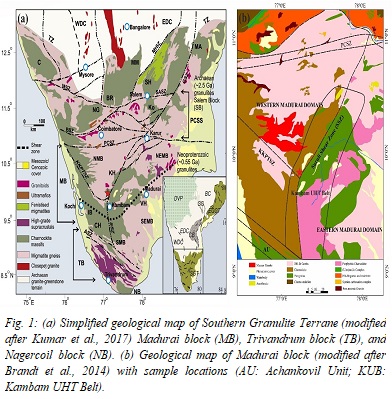 The Madurai block which forms the central crustal block in the Precambrian Southern Granulite Terrane, south India preserves crustal evolution history with record of multiple magmatic and metamorphic episodes ranging from early Archaean to late Neoproterozoic. Documenting the precise chronology and tectonothermal evolution of these events are of paramount importance to correlate with other crustal blocks in Southern Granulite Terrane as well as to link with other continental fragments of East Gondwana. The present study focuses on hitherto unreported location within a key section of Madurai block along the transcrustal Suruli shear zone known as the Kambam ultrahigh-temperature belt. This belt is noticeable for the proliferous occurrence of HT-UHT metapelites with an overall clockwise P-T trajectory. Samples of garnet-spinel granulite, cordierite-spinel granulite and associated granite gneiss were subjected to detailed petrographic, thermobarometric and geochronologic analysis. Combined petrography, mineral reaction, geothermobarometry and pseudosection modelling of the granulite samples reveal HT-UHT metamorphic conditions with clockwise P-T path demonstrating significant decompression and cooling. LA-ICPMS U-Pb dating of zircon, monazite and rutile phases within these samples constrain the timing of metamorphism as well as cooling. U-Pb zircon ages of ~2500 Ma from the granulites points to new evidences for Paleoproterozoic high-grade metamorphism in the area where monazite U-Pb ages at ~593 and ~557 Ma throw light into the imprints on ~36 Ma prolonged Neoproterozoic thermal event attributed to Pan African collisional orogeny. LA-MC-ICPMS Hf isotopic record from zircon cores point to the role of significant juvenile crustal melting/anatexis during Paleoproterozoic. In addition, several cryptic metamorphic pulses are also identified evincing the polydeformed evolutionary history of these rocks. The ca. ~432 Ma cooling age record from rutile estimates an average cooling rate of ~3.0 °C/Ma over a time period of ~125 Ma, classifying Madurai block as a classic slow cooled granulite terrane with long lived UHT orogenic history. The results also bring to the fore the importance of Kambam ultrahigh-temperature belt and Suruli shear zone which can be projected as a major terrane boundary within the Southern Granulite Terrane.
The Madurai block which forms the central crustal block in the Precambrian Southern Granulite Terrane, south India preserves crustal evolution history with record of multiple magmatic and metamorphic episodes ranging from early Archaean to late Neoproterozoic. Documenting the precise chronology and tectonothermal evolution of these events are of paramount importance to correlate with other crustal blocks in Southern Granulite Terrane as well as to link with other continental fragments of East Gondwana. The present study focuses on hitherto unreported location within a key section of Madurai block along the transcrustal Suruli shear zone known as the Kambam ultrahigh-temperature belt. This belt is noticeable for the proliferous occurrence of HT-UHT metapelites with an overall clockwise P-T trajectory. Samples of garnet-spinel granulite, cordierite-spinel granulite and associated granite gneiss were subjected to detailed petrographic, thermobarometric and geochronologic analysis. Combined petrography, mineral reaction, geothermobarometry and pseudosection modelling of the granulite samples reveal HT-UHT metamorphic conditions with clockwise P-T path demonstrating significant decompression and cooling. LA-ICPMS U-Pb dating of zircon, monazite and rutile phases within these samples constrain the timing of metamorphism as well as cooling. U-Pb zircon ages of ~2500 Ma from the granulites points to new evidences for Paleoproterozoic high-grade metamorphism in the area where monazite U-Pb ages at ~593 and ~557 Ma throw light into the imprints on ~36 Ma prolonged Neoproterozoic thermal event attributed to Pan African collisional orogeny. LA-MC-ICPMS Hf isotopic record from zircon cores point to the role of significant juvenile crustal melting/anatexis during Paleoproterozoic. In addition, several cryptic metamorphic pulses are also identified evincing the polydeformed evolutionary history of these rocks. The ca. ~432 Ma cooling age record from rutile estimates an average cooling rate of ~3.0 °C/Ma over a time period of ~125 Ma, classifying Madurai block as a classic slow cooled granulite terrane with long lived UHT orogenic history. The results also bring to the fore the importance of Kambam ultrahigh-temperature belt and Suruli shear zone which can be projected as a major terrane boundary within the Southern Granulite Terrane.
Bibliographic Info: Amal Dev, J., Tomson, J. K., Nilanjana Sorcar, Nandakumar, V. [2021]. Combined U-Pb/Hf isotopic studies and phase equilibrium modelling of HT-UHT metapelites from Kambam ultrahigh-temperature belt, South India: Constraints on tectonothermal history of the terrane. Lithos, Vol. 406-407, Art. 106531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2021.106531
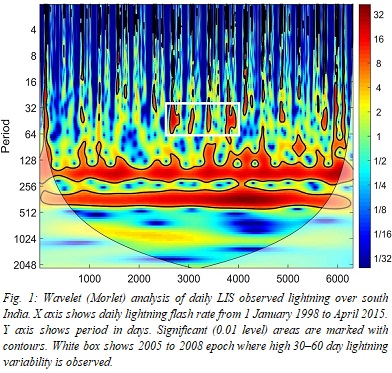 Lightning characteristics in India are examined with satellite-based Lightning Imaging Sensor (LIS) and ground-based Indian Lightning Detection Network (ILDN). LIS observations indicated that synoptic weather systems are major contributors of lightning in Indian hotspots. Western disturbances (mid-tropospheric systems with extratropical origin) were the greatest contributor of lightning in the Himalayas (93%), tropical cyclonic storms and low-pressure systems (oceanic in origin) were key lightning contributors in parts of eastern India (43%), and lower tropospheric troughs were major contributors in other hotspots. For the first time, this study reported the occurrence of significantly high lightning activity before active monsoon spells in the Central India region (65–87° E, 18–27° N). Consequently, satellite-based lightning observations could be used to predict active monsoon spells. Harmonic analysis was used to study diurnal lightning-flash density. The maximum observed standardized diurnal amplitude of lightning activity was 0.35, and maximum explained diurnal variation was 15%. Also, for the first time, we compared the ILDN data and LIS observations, and found good agreement regarding lightning variability. LIS data showed an increase in annual lightning activity in tropical South-western India (SWI), and the results also suggested that during El Niño and negative Indian Ocean Dipole periods, SWI experiences above-average lightning activity.
Lightning characteristics in India are examined with satellite-based Lightning Imaging Sensor (LIS) and ground-based Indian Lightning Detection Network (ILDN). LIS observations indicated that synoptic weather systems are major contributors of lightning in Indian hotspots. Western disturbances (mid-tropospheric systems with extratropical origin) were the greatest contributor of lightning in the Himalayas (93%), tropical cyclonic storms and low-pressure systems (oceanic in origin) were key lightning contributors in parts of eastern India (43%), and lower tropospheric troughs were major contributors in other hotspots. For the first time, this study reported the occurrence of significantly high lightning activity before active monsoon spells in the Central India region (65–87° E, 18–27° N). Consequently, satellite-based lightning observations could be used to predict active monsoon spells. Harmonic analysis was used to study diurnal lightning-flash density. The maximum observed standardized diurnal amplitude of lightning activity was 0.35, and maximum explained diurnal variation was 15%. Also, for the first time, we compared the ILDN data and LIS observations, and found good agreement regarding lightning variability. LIS data showed an increase in annual lightning activity in tropical South-western India (SWI), and the results also suggested that during El Niño and negative Indian Ocean Dipole periods, SWI experiences above-average lightning activity.
Bibliographic Info: Unnikrishnan, C. K., Sunil Pawar, Gopalakrishnan, V. [2021]. Satellite-observed lightning hotspots in India and lightning variability over tropical South India. Advances in Space Research, Vol. 68 (4), pp. 1690-1705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.04.009
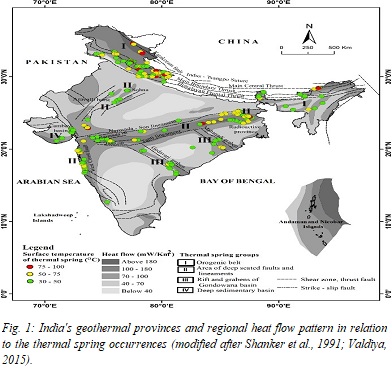 The widely distributed thermal springs in India are reviewed from a hydrogeochemical and isotopic perspective. Based on the geotectonic framework, the thermal springs are classified into four groups: (a) Orogenic belt, (b) Areas of deep-seated faults and lineaments, (c) Rifts and grabens of Gondwana basin and (d) Deep sedimentary basin. Detailed investigations over the last few decades culminated in the development of a vast geochemical database for thermal springs and associated gaseous phases, which are now available online since the late 1960s. After a careful evaluation of their quality and reliability, these data have been used in this study. Representative datasets of thermal spring waters from each group and subgroup have been evaluated following a classical approach, including water classifications, use of the triangular diagrams, geothermometric estimates and isotopic signatures that identified significant hydrogeochemical variations among different thermal spring clusters. Differences in rock-water interactions, and system characteristics such as water source, heat source, and topographic relief, were found to be the causes of observed variations. Thermal springs near the coast of western India have a high Cl content relative to Na, indicating that they have been influenced by seawater. Most thermal springs in the northern territory have high HCO3 and low Cl, suggesting that they have mixed with HCO3-rich near-surface water. Due to their emergence from the Precambrian crystallines, most thermal springs in the central and eastern part of India are distributed within the Na-Cl and Na-Cl-HCO3 type facies with low SO4 content. Different geochemical thermometers such as silica, cation thermometers, and a combination of silica K-Mg systems were used to estimate reservoir temperatures, resulting in a temperature range of roughly 60–140°C. Because of the lack of equilibrium, the values of reservoir temperatures between 200°C and 300°C obtained using Na-K geothermometers may not be reliable. In general, the reservoir temperatures for thermal springs in India's northern and eastern parts are greater than those located in the southern and western continental margins. The chemistry of the associated gaseous discharges is dominated by atmospheric components. The exceptions are thermal springs from the Orogenic belt of Himalaya that are enriched with CO2 possibly sourced from metamorphic decarbonation. The 3He/4He isotopic ratio in the gaseous discharge across all the groups and subgroups predominantly bears signatures of crustal origin. Stable isotopic signatures strongly suggest that these hydrothermal systems are predominantly recharged by local meteoric waters. In contrast, a discernible positive oxygen-isotopic shift in thermal waters indicates the existence of high enthalpy reservoirs in the NW Himalayan region. With the exception of a few springs, long circulation time (>50 years) of meteoric waters within the conduit is indicated by low tritium values in the thermal waters.
The widely distributed thermal springs in India are reviewed from a hydrogeochemical and isotopic perspective. Based on the geotectonic framework, the thermal springs are classified into four groups: (a) Orogenic belt, (b) Areas of deep-seated faults and lineaments, (c) Rifts and grabens of Gondwana basin and (d) Deep sedimentary basin. Detailed investigations over the last few decades culminated in the development of a vast geochemical database for thermal springs and associated gaseous phases, which are now available online since the late 1960s. After a careful evaluation of their quality and reliability, these data have been used in this study. Representative datasets of thermal spring waters from each group and subgroup have been evaluated following a classical approach, including water classifications, use of the triangular diagrams, geothermometric estimates and isotopic signatures that identified significant hydrogeochemical variations among different thermal spring clusters. Differences in rock-water interactions, and system characteristics such as water source, heat source, and topographic relief, were found to be the causes of observed variations. Thermal springs near the coast of western India have a high Cl content relative to Na, indicating that they have been influenced by seawater. Most thermal springs in the northern territory have high HCO3 and low Cl, suggesting that they have mixed with HCO3-rich near-surface water. Due to their emergence from the Precambrian crystallines, most thermal springs in the central and eastern part of India are distributed within the Na-Cl and Na-Cl-HCO3 type facies with low SO4 content. Different geochemical thermometers such as silica, cation thermometers, and a combination of silica K-Mg systems were used to estimate reservoir temperatures, resulting in a temperature range of roughly 60–140°C. Because of the lack of equilibrium, the values of reservoir temperatures between 200°C and 300°C obtained using Na-K geothermometers may not be reliable. In general, the reservoir temperatures for thermal springs in India's northern and eastern parts are greater than those located in the southern and western continental margins. The chemistry of the associated gaseous discharges is dominated by atmospheric components. The exceptions are thermal springs from the Orogenic belt of Himalaya that are enriched with CO2 possibly sourced from metamorphic decarbonation. The 3He/4He isotopic ratio in the gaseous discharge across all the groups and subgroups predominantly bears signatures of crustal origin. Stable isotopic signatures strongly suggest that these hydrothermal systems are predominantly recharged by local meteoric waters. In contrast, a discernible positive oxygen-isotopic shift in thermal waters indicates the existence of high enthalpy reservoirs in the NW Himalayan region. With the exception of a few springs, long circulation time (>50 years) of meteoric waters within the conduit is indicated by low tritium values in the thermal waters.
Bibliographic Info: Prasenjit Das, Maya, K., Padmalal, D. [2021]. Hydrogeochemistry of the Indian thermal springs: Current status. Earth-Science Reviews, Vol. 224, Art. 103890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103890




 सूचना का अधिकार
सूचना का अधिकार
