Uncategorised
Marine Science Group (MSG)

Scientists

Dr. L. Sheela Nair
Scientist G, Group Head, Marine Science Group (MSG)
Email : sheela[dot]lnair[at]ncess[dot]gov[dot]in
Phone(Off) : 0471- 2557900
Phone(Res) :
Fax : 0471-2442280

Dr. Reji Srinivas
Scientist E, Marine Science Group (MSG)
Email :reji[dot]srinivas[at]ncess[dot]gov[dot]in
Phone(Off) : 0471-2511760
Phone(Res) : +91-9846223737
Fax : 0471-2442280

Mr.Ramesh Madipally
Scientist D, Marine Science Group (MSG)
Email : ramesh[dot]madipally[at]ncess[dot]gov[dot]in
Phone(Off) :0471-2511671
Phone(Res) :
Fax : 0471-2442280

Dr. Prajith A
Scientist C, Marine Science Group (MSG)
Email : prajith[dot]a[at]ncess[dot]gov[dot]in
Phone(Off) : 0471-2511702
Fax : 0471-2442280
Scientific Support Staff

Rafeeque. M.K
Scientific Assistant Gr. B , Marine Science Group (MSG)
Email : rafeeque[dot]mk[at]ncess[dot]gov[dot]in
Phone(Off) :0471-2511689
Phone(Res) :
Fax :0471-2442280

Sreeraj M.K
Scientific Assistant Gr. B, Marine Science Group (MSG)
Email : sreeraj[dot]mk[at]ncess[dot]gov[dot]in
Phone(Off) :0471-2511689
Phone(Res) :
Fax :0471-2442280

Sreejith N
Scientific Assistant Grade A, Marine Science Group (MSG)
Email : sreejith[dot]n[at]ncess[dot]gov[dot]in
Phone(Off) :0471-2511716
Phone(Res) :
Fax :0471-2442280

Vibin.P.B
Scientific Assistant Gr. B, Central Geomatics Laboratory
Email : pb[dot]vibin[at]nic[dot]in
Phone(Off) :0471-2511652
Phone(Res) :

Lincy Sudhakaran
Scientific Assistant Gr. A, Marine Science Group (MSG)
Email :
Phone(Off) :
Phone(Res) :

Thin Section, Sample Preparation & Mineral Separation Facility
NCESS thin section laboratory consists of a complete range of equipment necessary for preparing thin glass slides of rock/mineral samples. The laboratory is equipped with automatic thin section preparation units from Buhler USA (Isomet 1000, Isomet 5000, PetroLap, PetroBond, PetroThin, PetroPol, Automet), Struers-Labpol, Section grinding machine (Geological Syndicate, Calcutta), rock cutting machines for both big block samples and smaller specimens, and mounting press. The laboratory has the capabilities to prepare thin sections (up to ~0.03 mm) from hard rocks, weathered materials, loose sand, silt etc. The facility is also well equipped to prepare polished sections for ore microscope study, microprobe work, fluid inclusion plates, and grain mounting. Routine works undertaken in the facility include preparation of normal (un-polished) and polished rock sections and grain mounts for petrographic studies and EPMA analysis and preparation of wafers for fluid inclusion studies. The standard operating procedure involves three steps; sectioning, grinding and polishing. In between each step the samples will be cleaned using Sonic Clean ultrasonicator.
For the preparation of finely powdered samples used for whole-rock major and trace element geochemical analysis, the facility has a Fritsch Pulverisette with Ni-Ch grinding set (Fritsch GmbH; Germany) attached with air compressor, Jaw Crusher (Insmart Systems) and Hydraulic crusher unit.
The mineral separation facility includes Holman-Wilfley wet shaking table, Exhaust fume hood for heavy liquid separation, Frantz magnetic barrier separator (LB-1) and Binocular microscope (Nikon) with a camera attachment. The laboratory routinely processes the separation of different accessory mineral phases such as zircon, monazite, rutile, baddeleyite etc. The separated minerals are mounted on epoxy discs, ground and polished for further analysis in NCESS Isotope Geochemistry Facility.
Thin Section Preparation Units

Sample Powdering Units
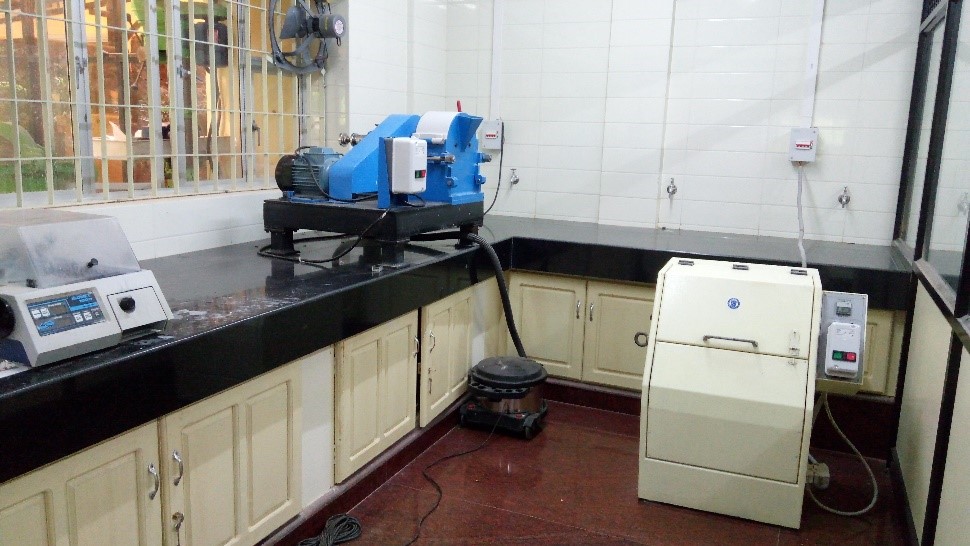

Holman-Wifley Wet Shaking Table
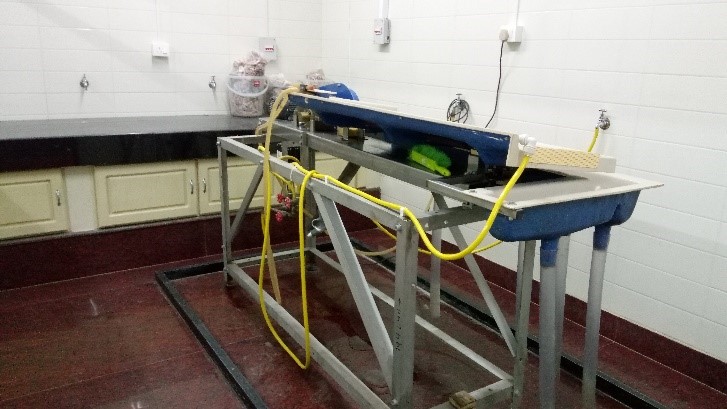

Frantz LB-1 Separator & Binocular Stereomicroscope

Contact
The Group Head, SERG
Palaoemagnetism laboratory
The palaeomagnetism laboratory was built during 1989-1990 and is being upgraded with full financial assistance from grants of the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India. The laboratory is equipped with a spinner magnetometer (sensitivity 0.05 mA/m; long spin; MOLSPIN Ltd, UK), AF demangetiser (peak field 100 mT; MOLSPIN Ltd; UK), MMTD thermal demagnetiser (Magnetic measurements, UK). The laboratory also has low field hysterisis apparatus, High field hysterisis loop tracer, pulse field magnetometer (Arun Electronics Ltd; Bombay) to record rockmagnetic properties. The spinner magnetometer is interfaced to an IBM personnal computer. The laboratory is equipped, for field collection of samples, with two Pomeroy gasoline drills (ASC scientific; USA), diamond drill bits, oriented device, pump can for water cooling, Brunton compass and other accessories. Laboraratory drilling Unit (Bharat Diamond works Ltd; Bombay) is also available for drilling and preparing specimens for palaeomagnetic study.

Petrology Laboratory (PL)
NCESS Petrology laboratory is equipped with the latest research model microscopes like Zeiss trinocular polarising microscope- AxioVision; Leica binocular polarising microscope with Leica DFS 320 digital photographic system, Mechanical counting stage; Leica M205C Stereo binocular microscope with 20.5:1 zoom. These are in addition to a) Leica transmitted/reflected binocular petrographic microscope with MPS 60 photomicrographic system b) Zeiss transmitted/reflected binocular petrographic microscope, c) Zeiss monocular, polarizing microscopes. NCESS petrology laboratory caters to the needs of the various disciplines of Earth Science at NCESS and other Institutes and Universities for carrying out research in fundamental and applied aspects of igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic petrology.
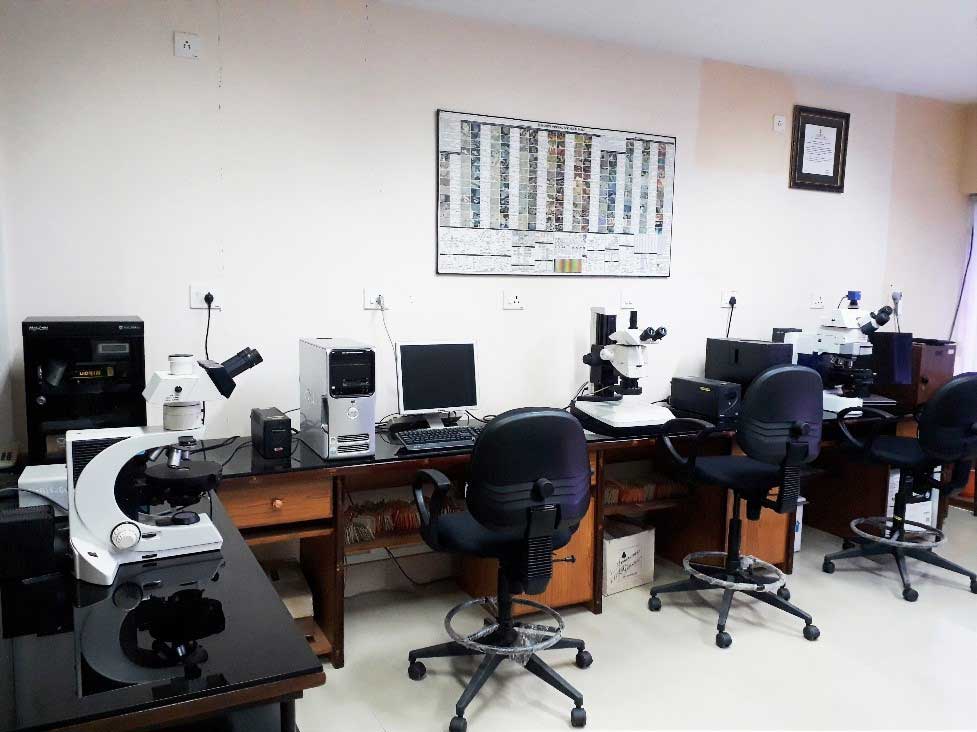


National Facility for Geofluids Research and Raman Analysis
National Facility for Geofluids Research and Raman Analysis in NCESS is equipped with the most advanced digital Laser Raman Micro spectrometer with three lasers (785 nm, 325 nm & 405 nm) suitable for Raman spectral analysis and Photo Luminescence (PL) studies. The system is installed as part of a multi-institutional collaborative project “Palaeo Fluids in the Petroliferous Basins of Western Offshore- India” sponsored by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), Govt. of India. The equipment is a high-sensitivity system with integrated research grade microscope, enabling high-resolution confocal measurements. With a comprehensive range of Rayleigh filter options, and motorised switching, it is easy to configure the system to suit various analytical needs.
What you can analyze?
Raman scattering with the Laser Raman Micro spectrometer system can characterize any solid, natural or synthetic material. Laser Raman Spectrometry for which doubly polished wafers used for fluid inclusion micro-thermometry are suitable can characterize fluid inclusions in minerals. Raman Spectra can be obtained on compact polycrystalline aggregates mounted on aluminium slides or embedded in a mould with the top surface polished. Powders/ Liquid samples can also be used.
Analytical briefs
Laser Raman Spectrometry can be done with 785 nm (300 mW), 405 nm (100 mW) and 325 nm (20 mW) (fixed wavelengths). With the use of motorized neutral density filters, we can work with 16 different power levels from 0.00005 to 100 percent of the actual Laser power. The spectral range of the equipment is from 50 cm-1 to 4000 cm-1 shift from the Laser line, accomplished with an edge filter. The Raman scattered light is dispersed with a grating and is having dual grating 1200 l/mm and 2400 l/mm. The detection is done by a Peltier cooled CCD detector with 576 x 384 pixels, with spectral resolution of 1 cm-1. The Raman system is fitted with XYZ mapping stage as well as confocal arrangement enabling imaging studies with spatial and depth resolutions of 1 and 2 µm respectively. The Renishaw Raman system has the flexibility for performing photoluminescence (PL) studies at two laser wavelengths. The system is fully automated and self-validating with auto aligning and optimization of input laser power. The operation of the equipment is fully software controlled.
Output
Results are distributed either as hard copy of the spectral traces or as soft copy of the spectral data (Intensity vs Raman Shift at 0.25 cm-1 interval/Intensity vs wavelength) in CD supplied by the user.




 RTI Act
RTI Act